Everything You Should Know About Magnesium Glycinate
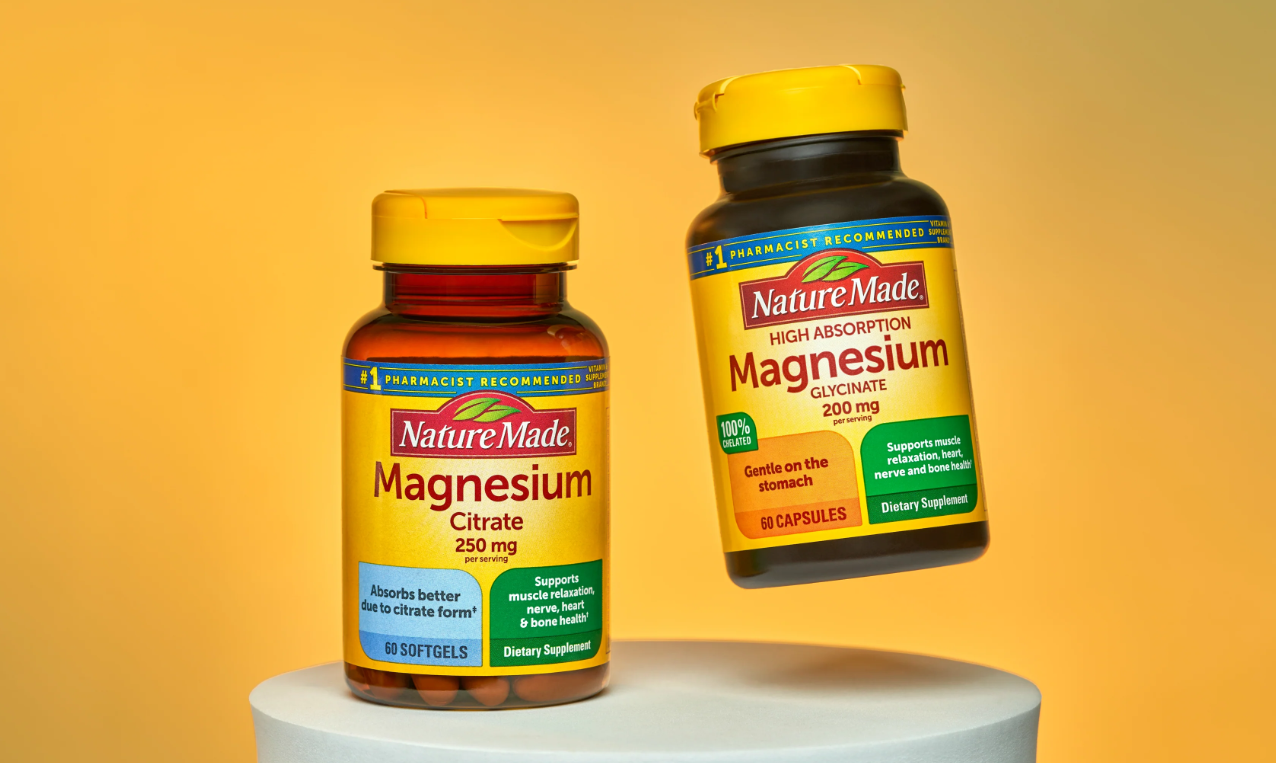

Magnesium Glycinate – Magnesium is an essential mineral in various bodily functions, from muscle and nerve function to bone health and energy production.
While magnesium can be obtained from various food sources like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, many people still struggle to get enough of it in their diets.
This is where magnesium supplements, particularly magnesium glycinate, come into play. This blog post will dive into everything you should know about magnesium glycinate.
Understanding Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate, also known as magnesium bisglycinate or magnesium diglycinate, is a magnesium salt of glycine, an amino acid. It is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium, easily absorbed and utilized by the body. This makes it a popular choice for individuals who require magnesium supplementation.
Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate
- Better Absorption: Magnesium glycinate is well-absorbed in the intestines, making it an excellent choice for those with digestive issues that may hinder magnesium absorption.
- Reduced Laxative Effect: Some magnesium supplements, like magnesium citrate, can have a laxative effect when taken in high doses. Magnesium glycinate is less likely to cause this side effect.
- Muscle Relaxation: Magnesium is known for its role in muscle function and relaxation. Magnesium glycinate can help alleviate muscle cramps and spasms.
- Improved Sleep: Many people find that magnesium glycinate promotes better sleep quality and may help with insomnia or restless leg syndrome.
- Mood and Stress: Some individuals report that magnesium supplementation, including magnesium glycinate, can be calming and may help with anxiety and stress management.
- Heart Health: Adequate magnesium intake is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular issues. Magnesium glycinate may help support heart health.
- Bone Health: Magnesium is essential for strong bones; magnesium glycinate can contribute to bone density.
Dosage and Usage
The recommended daily magnesium intake varies depending on age, sex, and individual needs. As a general guideline, adult men typically require around 400-420 mg of magnesium daily, while adult women need approximately 310-320 mg daily. Pregnant and lactating women may need more.
When it comes to magnesium glycinate supplementation, following the dosage instructions provided on the product label or consulting with a healthcare professional is essential. Dosages typically range from 100 mg to 400 mg per day, depending on the intended use and individual requirements.
Potential Side Effects
Magnesium glycinate is generally well-tolerated, and side effects are rare. However, taking very high doses can lead to gastrointestinal issues like diarrhoea. If you experience any adverse effects, you should reduce the dosage or consult a healthcare provider.
Interactions and Precautions
Before starting any new supplement regimen, it’s crucial to consider potential interactions with medications or underlying health conditions. Magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, so consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium
While magnesium glycinate supplements can be a convenient way to boost your magnesium intake, it’s also important to include magnesium-rich foods. Some good dietary sources of magnesium include:
- Leafy green vegetables (e.g., spinach, kale)
- Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, pumpkin seeds)
- Legumes (e.g., beans, lentils)
- Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa)
- Avocado
- Bananas
Risks of taking magnesium
While magnesium is an essential mineral with numerous health benefits, excessive magnesium supplements or medications can lead to potential risks and side effects. Maintaining a balance and ensuring you’re not exceeding the recommended daily intake is crucial. Here are some of the risks associated with excessive magnesium intake:
Gastrointestinal Issues:
High magnesium supplements can cause digestive problems such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Magnesium supplements with laxative effects, such as magnesium citrate or magnesium hydroxide, are particularly likely to cause these issues.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Magnesium is an electrolyte, and excessive intake can disrupt the balance of electrolytes in your body, particularly when taken alongside other electrolyte-altering substances like diuretics. This imbalance can lead to symptoms like irregular heartbeat and muscle weakness.
Kidney Problems:
People with impaired kidney function may be at greater risk of magnesium accumulation in the body, as the kidneys are responsible for excreting excess magnesium. If you have kidney issues, consult your healthcare provider before taking magnesium supplements.
Low Blood Pressure:
High doses of magnesium can lower blood pressure, which may be problematic for individuals with already low blood pressure or those taking medications that lower blood pressure.
Medication Interactions:
Magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. These medications may include antibiotics, diuretics, and medications used to manage heart conditions. Consult with your healthcare provider if you are taking any of these medications.
Respiratory Issues:
Inhaling magnesium-containing dust or aerosols, such as during industrial processes, can lead to respiratory issues, including coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Hypermagnesemia:
In rare cases, excessive magnesium intake, usually from very high-dose supplements, can lead to hypermagnesemia. Symptoms may include muscle weakness, lethargy, confusion, and, in severe cases, cardiac arrest.
To avoid these risks and ensure you receive the benefits of magnesium without adverse effects, it’s essential to:
- Follow Dosage Recommendations: Adhere to the recommended daily intake guidelines for magnesium, and consult your healthcare provider before taking high-dose supplements.
- Monitor Symptoms: If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking magnesium supplements, consult a healthcare professional. It’s important to address any side effects promptly.
- Consider Dietary Sources: Whenever possible, obtain your magnesium from dietary sources like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains. A well-balanced diet can help you maintain optimal magnesium levels without needing supplements.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: If you have specific health conditions or are taking medications, consult with your healthcare provider before adding magnesium supplements to your regimen. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health needs.
In summary, while magnesium is essential for overall health, excessive intake through supplements or medications can pose risks.
It’s important to strike a balance and use magnesium supplements cautiously, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications that may interact with magnesium.
Always seek professional medical advice when in doubt, and prioritize a balanced diet of magnesium-containing foods to meet your nutritional needs.
In Conclusion
Magnesium glycinate is a well-absorbed, versatile form of magnesium that offers numerous health benefits. Whether you want to improve muscle function, sleep quality, or overall well-being, magnesium glycinate may be a valuable addition to your supplement routine.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement to determine the right dosage and ensure it’s appropriate for your needs. Additionally, remember that a balanced diet rich in magnesium-containing foods is essential for maintaining optimal health.
FAQs:
1. What is magnesium glycinate, and how does it differ from other magnesium supplements?
- Answer: Magnesium glycinate is a magnesium salt combined with the amino acid glycine. It is highly bioavailable and less likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects compared to some other magnesium supplements like magnesium citrate or magnesium oxide.
2. What are the potential benefits of taking magnesium glycinate?
- Answer: Magnesium glycinate may provide benefits such as improved sleep, muscle relaxation, stress reduction, and support for heart and bone health. It is also known for its better absorption compared to other magnesium forms.
3. How much magnesium glycinate should I take daily?
- Answer: The recommended daily dosage can vary based on individual needs and health conditions. Generally, doses of magnesium glycinate range from 100 mg to 400 mg per day. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for your situation.
4. Can I take magnesium glycinate with other medications?
- Answer: Magnesium supplements, including magnesium glycinate, can interact with certain medications. If you are taking any medications, particularly antibiotics, diuretics, or medications for heart conditions, consult your healthcare provider before adding magnesium glycinate to your regimen.